
One of the many good companies
HUMAN
HAPLOGROUPS
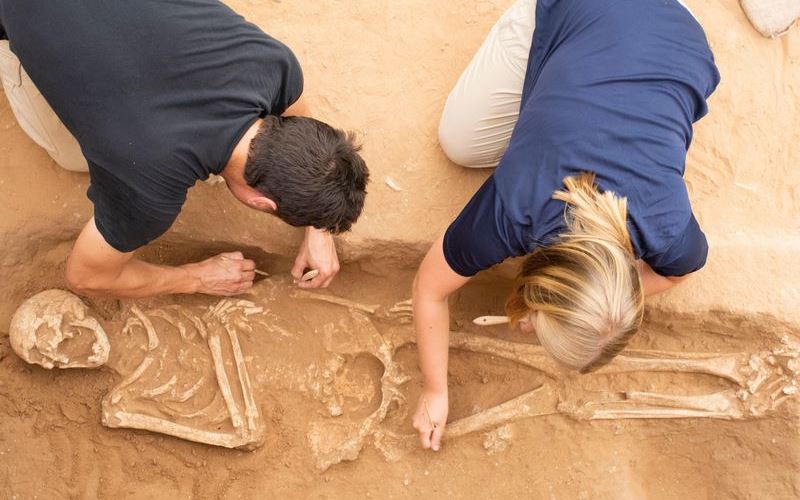

Excavation of the Philistine cemetery at Ashkelon

One of the many good companies |
HUMAN
|

Excavation of the Philistine cemetery at Ashkelon |
Y-DNA haplogroupsThe Y-DNA code A0000 is given to the Denisovans, and A000 to the Neanderthals. From them more than 100 SNPs are already known, all starting with an A letter. |
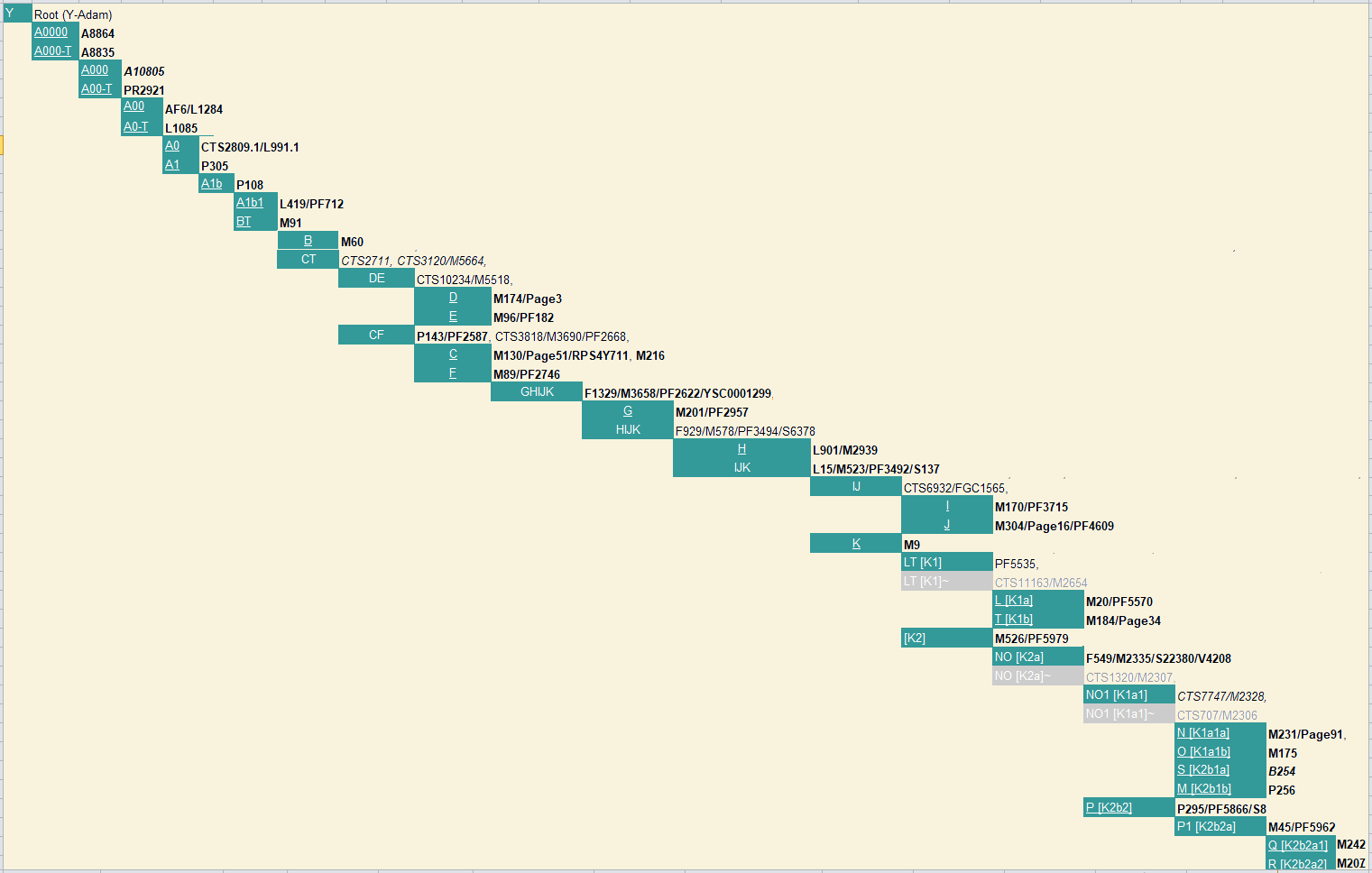
Y-Tree-ISOGG by Ray Banks. (1) |
|
* 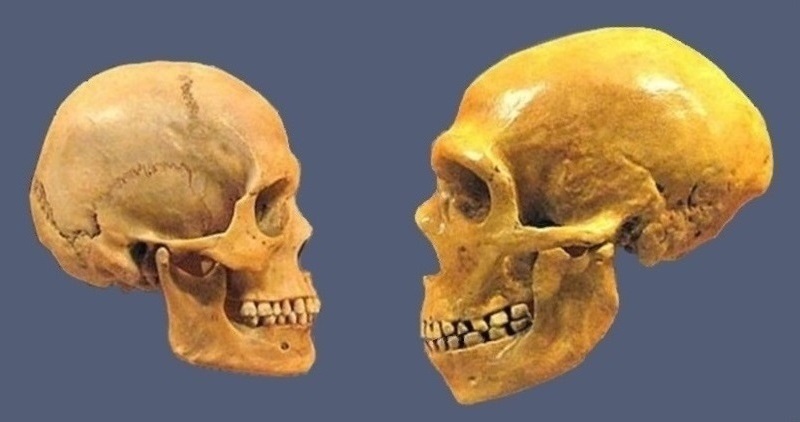
The skull of a homo sapiens and a Neanderthal. Museum of Natural History in Cleveland. (2) * Homo Sapiens comes from the Homo heidelbergensis, also known as Homo rhodesiensis, an species or subspecies of archaic humans in the genus Homo that is extinct in the Middle Pleistocene - about 700,000 years ago. Denisovans and Neanderthals split from Homo sapiens around 750,00 years ago and diverged from each other around 100.000 years later. 
Reconstruction Homo erectus from Georgia (3) * DenisovansA0000 - A8864 → A8983 * Neanderthals |
|
A000T
|
A8835
|
|
* Homo Sapiens Sapiens The oldest common human ancestor has been given the code A00. His direct descendants are now living in Cameroon in Africa. The estimated modern human-Neandertal TMRCA is 387 ka (95% HPD 344 to 432 ka).
The modern human TMRCA is estimated at 268.000 ybp (95% HPD 238 to 301 ka)
(4a)
All people in the world seem to descend from a woman that to alleged lived around 200.000 ybp in Africa, somewhat younger. All human Y-DNA haplogroups have sprouted from the common ancestor of all humans. He lived in Africa and had haplogroup A00-AF4. He lived about 250,000 ybp * Y-DNA Haplogroep A00-AF6/L1284.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup BT-M8968/PF207, M91, stems from A1b-Y8278. From this come the Haplogroups B-M60 and haplogroup CT-CTS2711. They are the ancestors of all Eurasian people, formed 130,700 ybp, TMRCA 88,000 ybp. * Y-DNA Haplogroup B-M8720/V2144 originated in Africa, formed 88,000 ybp, TMRCA 84,200. Stems from AT. This man and his descendants remained in Africa. They live there now scattered in small concentrations among hunter-gatherers of Ethiopia and Sudan, and at the click language speakers.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup CT-M5608/PF258, comes from BT-M8968/PF207. formed 88,000 ybp, TMRCA 68,500 ybpDescendants of Haplogroup CT have been found in various prehistoric human fossils that were analysed for ancient DNA, including specimens associated with the Pre-Pottery Neolithic C (1/1; 100%), Neolithic Ganj Dareh Iran (1/2; 50%), Natufian (2/5; 40%), Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (2/7; ~29%), Alföld Linear Pottery (1/1 at two ALP archaeological sites; 100%), Linearbandkeramik (1/2 at Karsdorf LBK archaeological site; 50%) cultures, and some Upper Paleolithic Europeans (Cioclovina1, Kostenki12, Vestonice13). But whether these, or all of them, belong to paragroup CT* or to its branches, is as yet undetermined.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup CF-M3711/CTS6376/PF2697 stems from CT-M168. Is formed 68,500 ybp, TMRCA 65,900 ybp From CF come the haplogroups C-M130 and F-M89. The clade's existence and distribution are inferred from the fact that haplogroups descended from CF include most human male lineages in Eurasia, Oceania and The Americas. * Y-DNA Haplogroup C-CTS1631, F2067, Y1785, formed 65900 ybp, TMRCA 48400 ybp stems from CF-M3711, arose shortly after the departure of the modern human from Africa. He travelled across the southern Arabian peninsula, through Pakistan and India, and on to Sri Lanka, Southeast Asia, Japan, Polynesia and Australia. Haplogroup C is found in ancient populations on every continent except Africa and is the predominant Y-DNA haplogroup among males belonging to many peoples indigenous to East Asia, Central Asia, Siberia, North America and Oceania. The haplogroup is also found at moderate frequencies among certain indigenous populations of Southeast Asia.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup DE-CTS10234, stems together with his bother clade CF-P143 from CT-CTS2711, the age of haplogroup DE is generally estimated between 65,000 and 71,000 years. DE is distributed in several geographically distinct clusters. From DE come the haplogroups D-M174 and E-M96. * Z1605/CTS4030 Y-DNA Haplogroup D-Z1605/CTS4030 stems from via DE-CTS10234, is formed 65200 ybp, TMRCA 46500 ybp, is now predominant in Central and Southeast Asia.
|
*
|
Y-DNA Haplogroup E-M96 comes from haplogroup DE-CTS10234. This is a brothergroop of D-M174. formed 65200 ybp, TMRCA 53200 ybp, spread over whole Africa with the Bantu agricultural expansion. E is also the most common lineage among African Americans. It is an old, diverse haplogroup with many branches and is found distributed throughout Africa today. It is also found at a very low frequency in North Africa and the Middle East He was one of the first emigrations of modern humans out of Africa His subgroup E1b1 has received the furthest branches and the largest distribution later in Africa and beyond. |
|
|
E1a1-M44, has been detected in the Fulbe population in Cameroon at 53%. 2-5% levels have been observed in Mali and Sudan, 18.9 KY. in Alsace-Lorraine.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup F-M89 stems from CF-P143, is formed 50,000 to 56,000 ybp most likely in the Indian Subcontinent, or somewhere close to it. He became the ancestor of all the Y-DNA haplogroups from G through T. His offspring now includes 90% of the world's population.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup GHIJK-F1329, stems from F-M89, formed 65900 ybp, TMRCA 48800 ybp, its subclades comprise the vast majority of the world's male population with the haplogroups G, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T. * Haplogroup G is described in detail at: Haplogroup G.
Y-DNA Haplogroup G-M201, stems from GHIJK-F1329, is formed in west Asia about 50,000 ybp and split in two subgroups G1 and G2 about 25,000 ybp. At present G is a small haplogroup in Europe with an occurrence from 3% to 7%, somewhat more at places in the Alps, and increasing to 10% on the islands of Sardinia and Corsica.
G1-M342 the oldest branch is formed in west Asia 25600 ybp TMRCA 18400 ybp.
G2-P287/PF3140, formed 25,600 ybp, TMRCA 20,800 ybp probably in the fertile crescent. G2a-P15/PF3112, ormed 20800 ybp, TMRCA 18000 ybp and started expanding after the Ice Ages, 14,500 ybp. Of the European archaelogical DNA 20% has these original clade; together with his subgroups they make 60% of the Earliest Neolithic European DNA. G2a1-FGC7535, Z6552 (former L293), formed 18000 ybp, TMRCA 18000 ybp its subgroups account for 50% to 70 % of the men in the Middle-Caucasus, and is also found among small groups of East Europeans, mostly Ashkenazic Jews and Lebanese Maronite Christians.
G2a2-L1259-CTS4367. is the ancestor of 90% of the European G. This group split into two, with G2a2a accounting for 10% of the European G, and G2a2b accounting for 80% of the European G. G2a2a-PF3147+ accounts for 5% of the European G and is found along the Danube, Rhine, Meuse and Thames, in Greece and Corsica and Sardinia. Furthermore, in South and Southwest Asia in Turkey Kurds and Armenians in Iran at Armenians in India.
G2a2b-L30/L32/U8/S126 is the major European trunk accounting for 80% of the G.
The first farmers in Europe had G2a and G2a2b Archaeologically found Y-DNA of the first settlers in Europe appeared to be G2a-P15 and G2a2b-L30. Before this time lived here hunter-gatherers who had C and I. Their first burial grounds are found at Derenburg in Sachsen-Anhalt(Germany). It is dated between 7.000 and 7,500 years ago.
Around 7000 years ago arrive this first in The Netherlands. They settle on the mountain slopes of the South Limburg Meuse Valley, as at Caberg a neighbourhood on the edge of the plateau west of Maastricht. Here is the fertile loess soil. They find blocks in the underground with flint for the manufacture of tools. Their pottery jars have the Linear Pottery style. The culture is flourishing for 500 years and then disappears without a trace. To what extent this culture disappeared together the population has not yet been demonstrated. There is difference of opinion whether the bringers of the new culture have absorbed or expelled the resident population. See also Maastricht Au-DNA .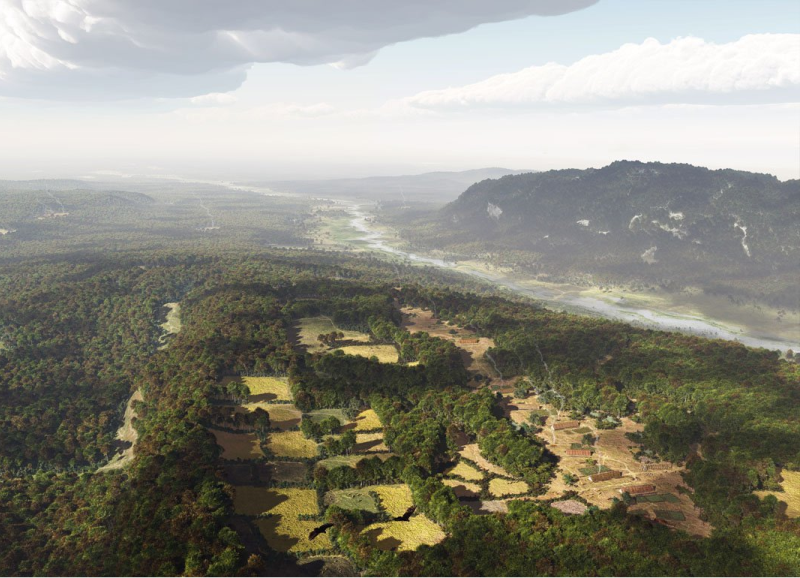 
Impression of a LBK hamlet at Caberg a neighbourhood on the edge of the plateau
* Y-DNA Haplogroup HIJK-F929, from this the haplogroups H-M69, IJ-FGC1665 and K-M9. * Y-DNA Haplogroup H-M69 arose out HIJK - F929/M578, most probably in India, 30.000 to 40.000 years ago. Today almost all carriers live in India. The European gypsies, called also the Roma or Sinti people, have this haplogroup ‑ they originally came from India.
H2-P96 Afghanistan, (till now) all have DYS393=14.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup IJK-L15 arose out HIJK - F929/M578, from this the haplogroups IJ-FGC1665 and K-M9. * Y-DNA Haplogroup IJ-FGC1665, derived populations account for a significant proportion of the pre-modern populations of Europe (especially Scandinavia and the Balkans), Anatolia, the Middle East (especially Arabia, The Caucasus, Levant and Mesopotamia) and coastal North Africa. As a result of mass migrations during the modern era, they are now also significant in the Americas and Australasia. * Y-DNA Haplogroup I-M170 formed 43.000 ybp is an European group, I1* is found in archaeological European finds. I* has been found in ancient Gravettian culture samples from Krems-Wachberg Austria dated to 31,000 cal BP. In the site of Balma Guilanyà in the Pyrenees, dated around 13,100 ybp (± 330y), nowadays it is present in about a fifth of the population and barely outside Europe. This suggests an origine in Europe, before the last glacial maximum.
I2-M438 is found in Armenia, Georgia and Turkey.
|
Y-DNA Haplogroup I1a |
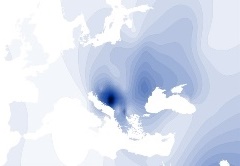
Y-DNA Haplogroup I1b |
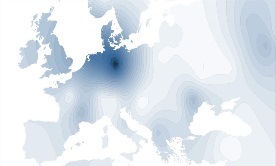
Y-DNA Haplogroup I1c |
*
|
Y-DNA Haplogroup J-P209 originated in Asia Minor and from there went to North Africa, Europe, Central Asia, Pakistan and India. Most come for J in the Middle East. The presence gradually decreases in the direction of Northwest Europe, where coastal residents have 3%. The distribution took place both in the Neolithic as well as by subsequent periodic waves of immigration. J1-L255/M267/PF4646 branches could have originated in the Levant and is now found in other parts of Asia Minor and North Africa, having spread along the southern Mediterranean and into Ethiopia. J2-L228/M172/S321 lines arose in the region along the Fertile Crescent, with its primary distribution probably occurring during the Neolithic period with the spread of agriculture in the Mediterranean region. It is not yet clear when J2 arrived in Central Asia, Pakistan, and India.
|
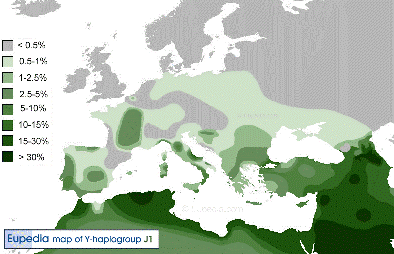
Y-DNA Haplogroup J1 |
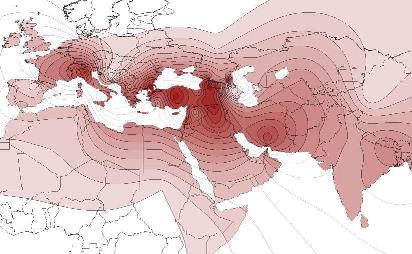
Y-DNA Haplogroup J2 |
*
|
Y-DNA Haplogroup K-M9 is an old line which arose about 50.000 years ago, probably in South Asia or West Asia. There are two branches: the first branch split into K1 through K4, which are found in low frequencies in Africa, Eurasia, Australia and the islands of the Pacific Ocean. From the second branch the haplogroups L to T sprouted.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup LT-L298/P326, PF5535 (former K1) divides into: L-M20 and T-M184. * Y-DNA Haplogroup L-M20
* Y-DNA Haplogroup M-P256 is found only in Papua, New Guinea, where it occurs in about 2/3 of the population. * Y-DNA Haplogroup N-M231 is distributed from southeast Asia to eastern Europe. The earliest finding of N in Europe comes from Iron Age Hungary, but is here virtually absent today.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup O-M175 is China's haplogroup, probably originating in southern China and from there spreading throughout China and to Taiwan, Indonesia and the Pacific islands.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup P-P295, M1254, sprung from K about 45.000 years ago in Central Asia and is now found in Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan and South Siberia. From it arose haplogroups Q and R, the dominant haplogroups of Europe and now also of America.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup Q-M242 comes from P1-M45, arose in Central Asia around 20,000 ybp and spread via the Altai-Baikal region of northern Eurasia to China and went about 16,000 ybp along the Bering strait to North America and South America. It is still found in its region of origin as well as among some Europeans.
* Y-DNA Haplogroup R-M207/Y482 comes from P1-M45 and is formed about 28.000 ybp. ago in Central Asia. It is both numerous and widespread amongst modern populations. Some descendant subclades have been found since pre-history in Europe, Central Asia and South Asia.
R1-M173/Y465, has been common throughout Europe and South Asia since pre-history. It has many branches, it has two major subgroups: R1a-L146/M420 and R1b-M343/PF6090. R1a-L146/M420/PF6229, , formed 22.800 ybp, TMRCA 18.200 ybp The cradle is very likely in the Eurasian steppe. Now it is most common in Eurasia, from Scandinavia and Central Europe to southern Siberia and South Asia.
R1b-M343/PF6242, formed 22.800 ybp, TMRCA 20.400 ybp,
R2-M479, formed 28.200 ybp, TMRCA 16.300 ybp, is found in Asia on the Indian subcontinent and in central Asia. Deep-rooted examples have also been found among Portuguese, Spanish, Tatar (Bashkortostan, Russia), and Ossetian (Caucasus) populations. R2 is present at low levels in the Caucasus, Iran, Anatolia and Europe. |
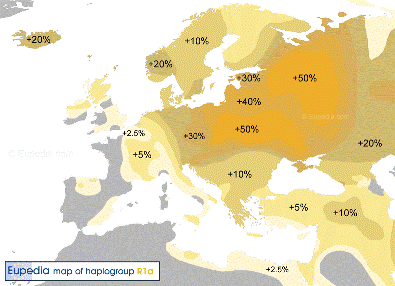
Y-DNA Haplogroup R1a |
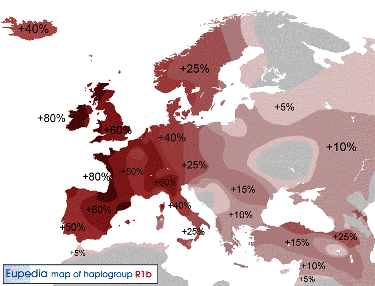
Y-DNA Haplogroup R1b |
*
|
Y-DNA Haplogroup S-M230 is the haplogroup of half of the population of the highlands of Papua, New Guinea. It is also found in low concentrations on neighbouring islands. * Y-DNA Haplogroup T-M184 is an immediate descendant of the haplogroup LT, whose parent clade is the haplogroup K. The clade arose 40,000 ybp. He is found at its highest frequencies among some populations in East Africa and East India. Is at frequencies of greater than 30% in Somalis of Djibouti, in Madagascar, Bauri, and Yerukula of East India, Argyns from Kazakhstan and rural Sciaccensis from Sicily.
Y-DNA Haplogroup T |
|
* Two shapes of the Homines Tree |
|
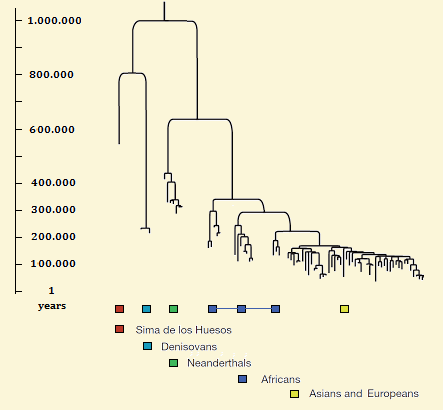
Homines tree (20) |
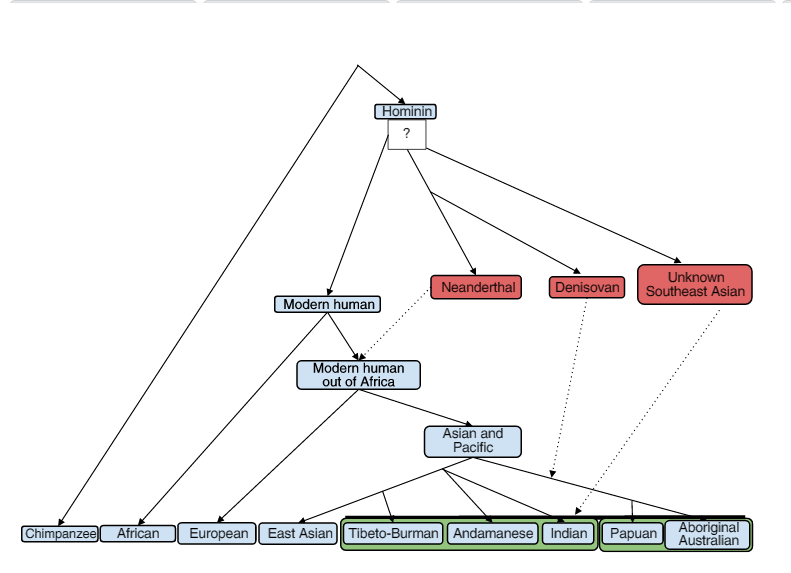
Genetic Tree of the hominides. (21) |
|
* Hypothetical Spread of Y-DNA in Europe during Pre-Roman Times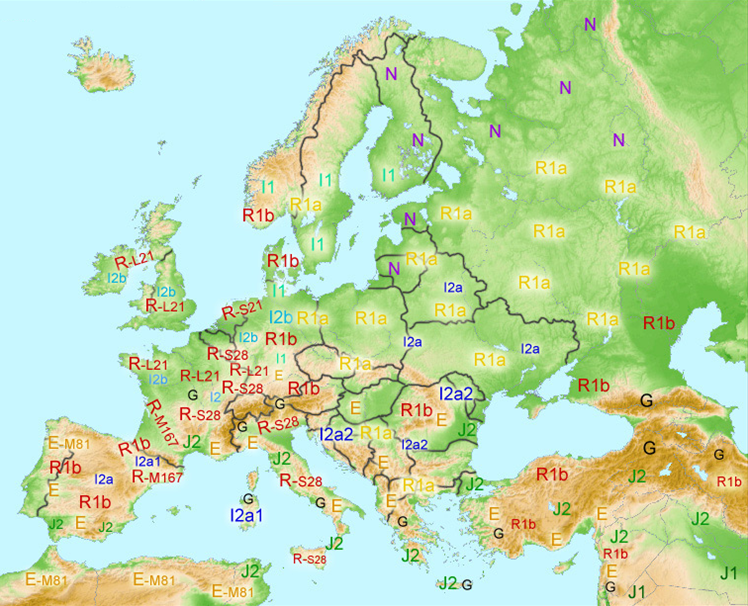
|
|
* World Map of Y-DNA Haplogroups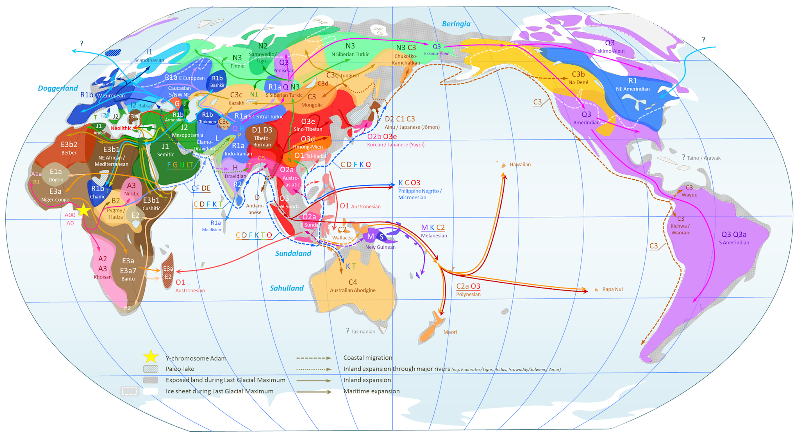
Hover your mouse over the map to see a magnification of Western Europe. (22) Please note that peoples do exist in which a single haplogroup decisively dominates, such as the native Americans or Bantu farmers, but most human groups show a mixture of various lineages in differing frequencies. For example, the wide distribution of haplogroup G ‑ which occurs throughout western Eurasia, but is dominant only in the Caucasus and in some populations of the Near East ‑ could not be deduced from this map. The labelling of R1 as "NE Amerindian" is peculiar, given the likely introduction of this lineage with European colonists, but in any case this only underscores the complexities of the present-day distribution of Y-chromosome haplogroups. |
|
* Mt-DNA HaplogroupsMitochondrial DNA (mt-DNA) is a tiny portion of the genome - only approximately 1/200,000th of it - which is passed down along the maternal line from mother to children and along the daughters to the grandchildren. The spread of mt-DNA haplogroups from Africa (Jean Manco) 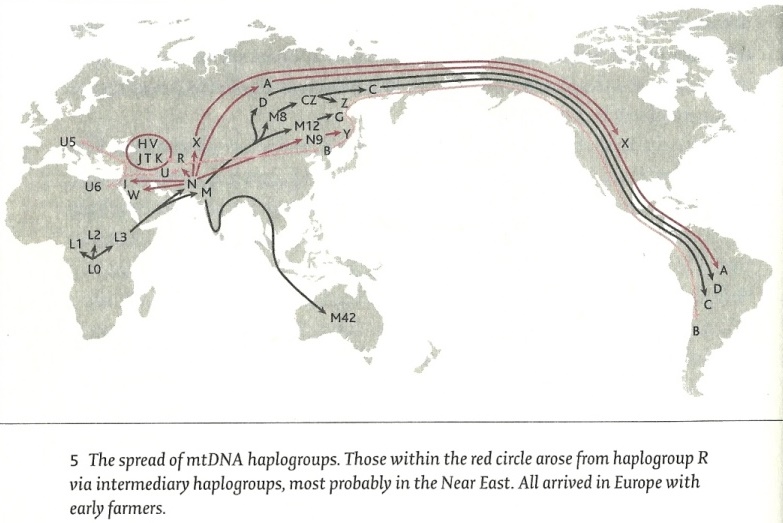
As a result of the sequencing of the complete Y-chromosomes of 69 males from nine populations and applying equivalent methodologies to the Y-chromosome and the mitochondrial genome the time to the most common Ancestor of the mitochondrial genome mt-TMRCA is estimated to be at 99.000 to 148.000 years. (23) * Mt-Haplogroup L0 is the clade of the woman who lived about 125.000 years ago in south or east Africa. All mitochondrial DNA lineages of humankind today are her descendants.
The women in the groups that arrived in Eurasia sixty thousand years ago had the haplogroups M and N. * Mt-Haplogroup M arose about 60 to 80,000 years ago, probably in East Africa, but possibly also in Arabia and spread together with N over Eurasia. In Europe, M disappeared during the last glacial maximum and was replaced by subclades of N. * From M arose the subgroups C, Z, D, E, G and Q. * Mt-Haplogroup N arose also about 70,000 years ago likely in Arabia Africa and is the mother mt-DNA haplogroup from which all present-day Europeans come. This group emerged in Africa and is still found in extremely low concentrations throughout the whole of Europe and Asia. Subgroups arose during the last Ice Age when they there were still hunter-gatherers.
* From N arose the subgroups O, A, S, R, I, W, X, Y, B, F, J, P, U, H, V, J, T and K. * Mt-Haplogroup C probably spread beyond its Ice Age refuge ‑ the area of Lake Baikal, the Yenisei River valley, and the Altai and Sayan mountains ‑ during the Mesolithic period. This haplogroup was among those carried by the potters of Lake Baikal about 7500 years ago.
* Mt-Haplogroup pre-HV, the precursor of the groups H and V has been extracted from a Cro-Magnon who lived 28.000 years ago in South-Italia. * Mt-Haplogroup H arose 35.000 years ago in central Asia and, with a 40% rate of occurrence, is the major mt-haplogroup in Europe today. It is noteworthy that the rate of occurrence in archaeological European DNA from 7,500 years ago is only half and, in Mesolithic material, hardly any at all.
(25)
* Mt-Haplogroup I arose about 20.000 years ago in the Near East or the Caucasus and dispersed in waves. One wave went to northern Europe, primarily Norway and Finland; another wave went to Pakistan and north-western India. It is still present in the Ukraine around the Caspian Sea, and in Anatolia and Greece. It seems to be connected with Proto-Indo-European culture, consequently accompanying Y-DNA R in particular R1a. but nothing is certain. Some think it may have been one of the foundation Mt-haplogroups of Europe which was later driven north and to other remote places. To date, Haplogroup I has not been found in samples taken from ancient European Palaeolithic, Neolithic, and Mesolithic grave sites, however it has been noted with significant frequency in more recent historic grave sites in Scandinavia. Its later dispersion would then be associated with the Vikings. The Croatian island of Krk is a "hotspot". * Mt-Haplogroup J is also an old haplogroup which arose 45.000 years ago in central Asia. It is thought to have come to Europe with Neolithic agriculture. Today it is commonly found in central Asia and north of the Caucasus. It seems to have some connection with Indo-European culture and the Y-DNA haplogroup R1b.
* Mt-Haplogroup K arose out of U8, and is found throughout the whole of Europe and western Asia to India. The highest concentrations are in northeast and central Europe, Anatolia and southern Saudi Arabia. It is thought to have emerged about 16.000 years ago in Egypt or Anatolia. Despite its relatively young age, it has the most subgroups.
* Mt-Haplogroup R arose from N and from these arose after the late glacial Maximum in Europe 6 mt-Haplogroups: pre-HV, T, U and K and the eastern subgroups R1 through R31 in Asia, Australia and the Americas. * Mt-Haplogroup T originated about 15.000 years ago in Mesopotamia or north-eastern Africa. Today it is found in northern Europe, northern Africa, Central Asia, and Siberia, with foci in India and northwestern China.
* Mt-Haplogroup U arose about 60.000 years ago from a woman in the mt-DNA Haplogroup R branch. This has been the only ancient DNA found in Europe dating from 30.000 to 5600 years ago. About 5000 years ago it was abruptly replaced by a very rich mt-DNA diversity of the Neolithic farmers.
(26)
* Mt-Haplogroup V presumably arose on the Iberian peninsula 15.000 years ago, during the last glacial period, among the hunter-gatherers who had withdrawn there with H1, H3 and U5 men. When the climate improved, they repopulated Europe. Today they constitute a large group, with the highest concentrations being found in northern Scandinavia among the Lapps (40%), and rates descending as one moves south, with the Netherlands at 8%. * Mt-Haplogroup W arose 18.000 years ago, with a spread similar to that of mt-Haplogroup I. Today it is found in the Ukraine, European Russia, the Baltic states and Finland, where it occurs in 3% to 5% of the population. In North Pakistan its rate of occurrence is 15%, and in North India, 10%, mostly among the higher castes and Indo-European speakers, and often paired with Y-DNA R1a and R1b. * Mt-Haplogroup X is more than 30.000 years old and is found in low concentrations in every population in Europe and northern Africa, and among the American Indians. The rates of occurrence are usually 1% to 2 % and rarely above 5%.
|
*
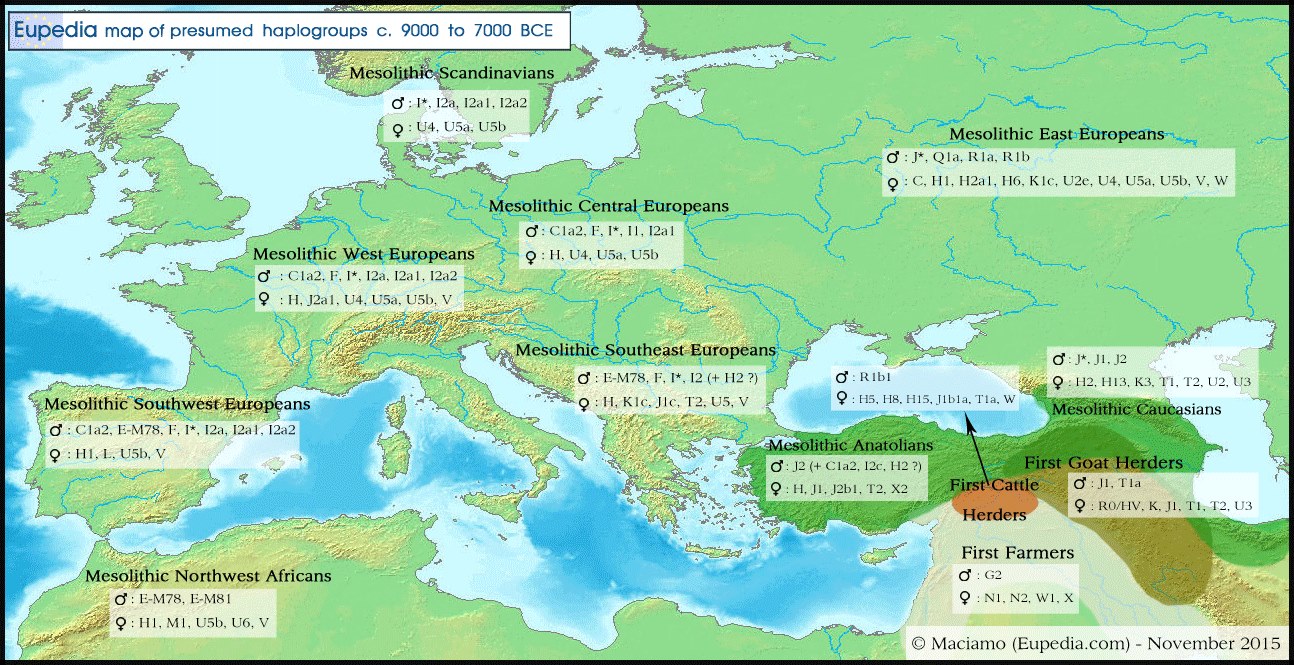
Distribution of Y-DNA and Mt-DNA haplogroups in Eurasia circa 9000 to 7000 BCE.
|
* What we are in the NetherlandsThe pie charts below show the distribution of the ten largest Y-DNA haplogroups in the Netherlands at 410 men in 2008, and in the Oud Hertogdom Brabant Project in Flanders among 1057 men in 2013. The differences between Belgium and the Netherlands are slightly distorted due to the participation of a small number of southern Dutchmen in the Belgian project. In the Belgian project, there was also an under-participation of French-speaking Walloons. 70% of all participants belonged to only four sub-haplogroups: R1b1b2a1 (R-U106), R1b1b2a2* (R-P312*), R1b1b2a2g (R-U152) and I1* (I-M253*). Significant micro-geographical differentiation within the sampling region was detected, mainly between the Dutch (Noord-Brabant) vs. the Flemish regions based on the differences in sub-haplogroup frequencies but not based on the Y-haplotype data within the main sub-haplogroups. A clear gradient was found with higher frequencies of R1b1b2 (R-M269) chromosomes in the northern vs. southern regions, mainly related to a similar trend in the frequency of R1b1b2a1 (R-U106). The genetic pattern faded away during the last centuries but was still detectable in 1950 according to the genealogical data. Nevertheless, the significant genetic differentiations and the clear gradient is not observable any longer in the contemporary population, most likely due to our higher mobility opportunities. (28) |
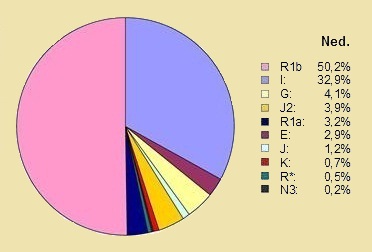
Netherlands |
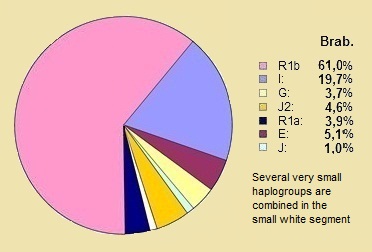
Belgium |
The Differences The differences between the two countries are quite clear in both haplogroup R1b and I.
* New Culture ‑ New Genes |
Mesolithic DNAThe oldest archaeologicafound Y-DNA is C-M130* It is found in a 37,000 years old skeleton in Kostenki on the Middle Don River in Russia. now still in Australia. From an European hunter-gatherer, who died 7000 years ago in La Brañaa, in Spain, could also ample DNA be determined: mt-DNA, autosomal and Y-DNA.
|

|
|
Curiously, it now seems that both Europe and India were (in part) inhabited by brown people and became lighter by a process of admixture + selection. The process went "all the way" in Europe, but a cline of pigmentation was sustained in India. (30) Neolithic DNAAn abrupt shift is 7200 years ago (before present, ybp) with the arrival of the first Neolithic farmers. This is found in Germany and Hungary, With their dominant haplogroup G2a and its subgroups G2a2b and G2a2b. The oldest European mummy, which was found in a glacier in Tyrol in the Ötzenthal and lived there 5300 years ago had G2a2a1b1a1-FGC5672 and mt-DNA haplogroup K1. A family from Thuringia in Lower Franconia, Bavaria, still has the same Y-DNA clades. Bronze Age DNAAround 6,800 ybp. We see at the beginning of the Bronze Age another shift. In a short period Haplogroup G is largely supplanted by a population of highly successful metalworkers and horse breeders. They have the Y-DNA haplogroup R. The northern branch R1a, the southern R1b They came from the Yamna culture in Southern Russia. R1a brought the Corded ware or Battle axe culture which lasted from 5000 to 4300 ybp. This new population spoke the Proto-Germanic language. The question is whether there has been genocide or displacement. It appears that half of the current European population are descendants of a single man, a king of this people with Y-DNA at the beginning of haplogroup R. Iron Age DNAAbout 4.000 ybp, at the beginning of the Iron Age, a change in mt-DNA occurred in Europe. This was coincidental and was probably related to the beginning of the dry era in the Middle East, following the long wet period on the Arab peninsula which had lasted from 8,500 to 4,500 years ago. Roman TimeA multitude of all Y-DNA clades happens, There is increasing prosperity throughout Europe concomitant with increased mobility of all kinds of people. * The dramatic Y-DNA changes in the NeolithicIn contrast to demographic reconstructions based on mt-DNA, we see a strong second bottleneck in the Y-chromosome lines in the last 10,000 years. The assumption is that this problem is caused by cultural changes affecting variance of reproductive success among males. We think of social stratification together with polygamy. The first was the out-of-Africa bottleneck in the Eurasian founder haplogroups in the narrow time interval at 47 to 52 kya. The Y chromosome plot suggested a reduction at around 4000 to 8000 years, when the female number is up to 17-fold higher than the male Number. (31) 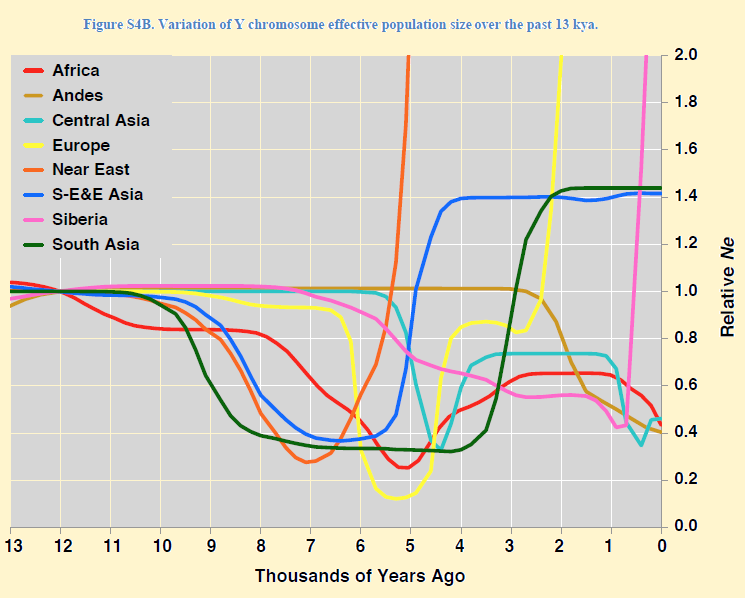
The dramatic events in the Neolithic, Bronze and Iron Age.
* Replacement of mt-DNA
|
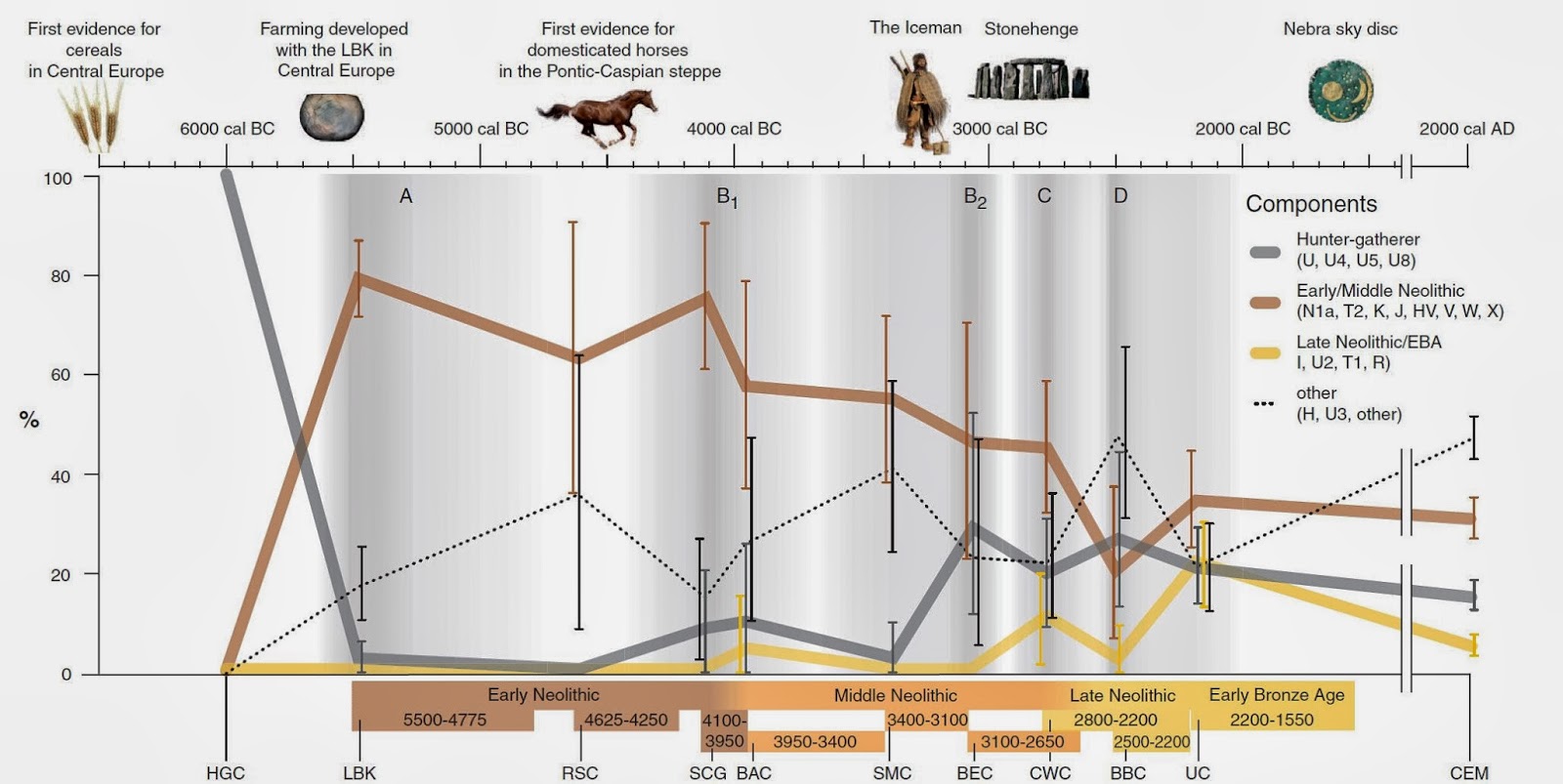
MtDNA Timelines
* ResumeWe see in the population history of Europe following successive populations: (35) |
|
Population 1. Neanderthals.
|
Starting time circa 200.000 years ago
|
End time circa 44.000 ybp
|
|
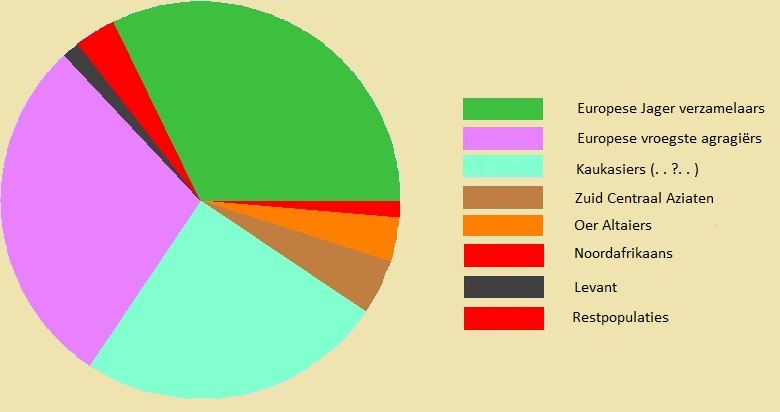
* Autosomal DNA (Au-DNA) in a Maastrichtian In this Maastrichtian are present the genes of all the peoples of the European prehistory.
|
|
Hunter-gatherers
|
32%
|
 |
|
* Recent replacement of the Y-DNA in CubaA good example of the displacement of native genes by a new set shows the genographic composition of the Caribbean island of Cuba. The island has been inhabited for 7,000 years. In 1513 it became a Spanish colony. At that time the Island had about 110,000 inhabitants. Now there are more than eleven million. The newcomers were Spanish but also many Africans, who came as slaves into the country. In 2012 an admixture analysis is made of a group of 1019 non-selective chosen people. To do this, a mixture of autosomal, Y-DNA, and mt-DNA haplogroup diagnostic markers is used. They found that the original Y-DNA haplogroups have almost entirely disappeared. for nearly 99½. Of mt-DNA haplogroups disappeared two thirds. In the imported population of black slaves this process occurred also, but to a much lesser extent. Their Y-DNA is still half their mt-DNA. (36) The conclusion that can be drawn is that at a relatively peaceful domination the initial male DNA almost completely disappears, but the female DNA to a large extent remains. When the latter disappears there will have been an extermination. 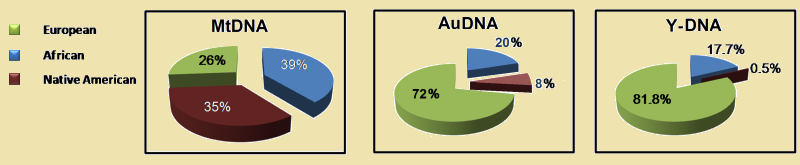
|
|
|
Mt-DNA
|
Autosomal DNA
|
Y-DNA
|
|
Example: This study has a significance that goes far beyond this island alone. Dominant new populations, anywhere in the world and in all times, will have bred with the women of conquered peoples. Of the subject men only a small part could have been able to maintain. Small Y-DNA haplogroups may be traces of an initial population. The small clades of Haplogroup G may be remnants of some ancient overrun native populations. |
|
* Searching for our anthropological background with Great DNA ProjectsWith the aid of data in large databases, one can discover the countries in which a particular haplogroup (or better, a subgroup) figures. As more tests are done, one will be able to look more deeply into our background. It is already becoming increasingly clear where certain subgroups originated and which peoples are characterized by each: Celts, Frisians, Franks, Burgundians, Saxons, Vikings, Vandals, Alans, Huns, Lombards, etc. FTDNA ‑ the Big Y projectThe Big Y test of FTDNA sequences a much larger part of the Y chromosome than done previously by either the standard Y marker (STR) testing, or the Geno 2.0 chip. The first results are now known. Full Genomes Sequencing The Full Genomes Sequencing is a high-coverage test, which basically tests all testable chromosome locations, perhaps 25 million in total.
|
|
|
 |
|
Litterature: - ISOGG.org/tree.
|
|
|
|